Table Of Content
It puts a focus on finding design solutions that get to the root of why a user or product problem occurs, rather than focusing on fixing the problem alone. Design thinking tends to be non-linear and iterative in its process to identify areas for improvement at each step of design. UX, UI and product designers may utilize design thinking to develop products and services that effectively address user needs. Microsoft, the world’s leading supplier of systems software, has been a technology-driven organization for a long time. Currently, Microsoft is using design thinking to focus on the user needs and user experience.
Learning Design Thinking
Framework for Innovation - Design Council
Framework for Innovation.
Posted: Thu, 11 May 2023 08:34:55 GMT [source]
Now you know what design thinking is and how it can be applied to almost any context. If you’re keen to start incorporating design thinking into your work right away, check out these nine design thinking tools to try with your team. If you’re going to adopt a design thinking framework, it’s wise to do an internal audit of your staffing needs, said Marcello Magalhaes, founder and chief design officer at brand design firm Speakeasy. His firm helps clients like Coca-Cola, Fanta, McDonald’s and Burger King find the right creative talent for special product launches and branding campaigns — roles that often don’t exist in-house. Design thinking can be applied to almost any project to tackle a problem. To start, here’s a few ways to implement design thinking in product development or beyond.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!
Design Thinking for CX Explained - CMSWire
Design Thinking for CX Explained.
Posted: Fri, 31 Mar 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
By unpacking the intuitive processes that designers use, even teams with a range of design experience stay on the same page. The prominence of Design Thinking in business is largely due to its ability to solve “ill-defined” problems effectively. Also called wicked problems, these problems typically involve human needs which can’t be easily modelled as systems of inputs and outputs. Wicked problems are inherently ambiguous and can be difficult to discuss and compare. Design thinking isn’t reserved for designers alone – it’s a mindset that anyone can cultivate to enhance problem-solving skills and drive innovation in their work and daily lives. Ingrained thinking occurs when people develop patterns of thought based on their routine and familiar situations.
Phase 5: Test

When we looked back over our shoulder, we discovered that there was a revolutionary movement behind us. The ambiguity rule of design thinking states that ambiguity is inevitable — you’re not going to have all of the answers, especially at the start. You can’t remove ambiguity either, so it’s best to embrace it by experimenting and exploring unknowns.
Prototype your ideas.
The round robin brainstorming exercise is a collaborative session where every person contributes multiple ideas. This is a great way to come up with lots of different ideas and solutions in the ideation stage of design thinking, where you’re focusing on quantity and creativity. To get the most out of a design thinking exercise, you’ll need a collaborative and creative mindset within your team. The team needs to be willing to explore new ideas, and laser-focused on customer or user needs. In order for this approach to be adopted across large organizations, it needed to be standardized.
What Are the 5 Phases of Design Thinking?
Once you give a prototyped solution to consumers, you must observe how they interact with it. This testing stage is the one in which you collect feedback on your work. In this second stage, you gather your observations from the first stage to define the problem you’re trying to solve. Think about the difficulties your consumers are brushing up against, what they repeatedly struggle with, and what you’ve gleaned from how they’re affected by the issue. Once you synthesize your findings, you are able to define the problem they face. There are many applications to using design-based thinking that apply outside of typical artistic fields.
Try Nintex Process Platform
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing. Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements. We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
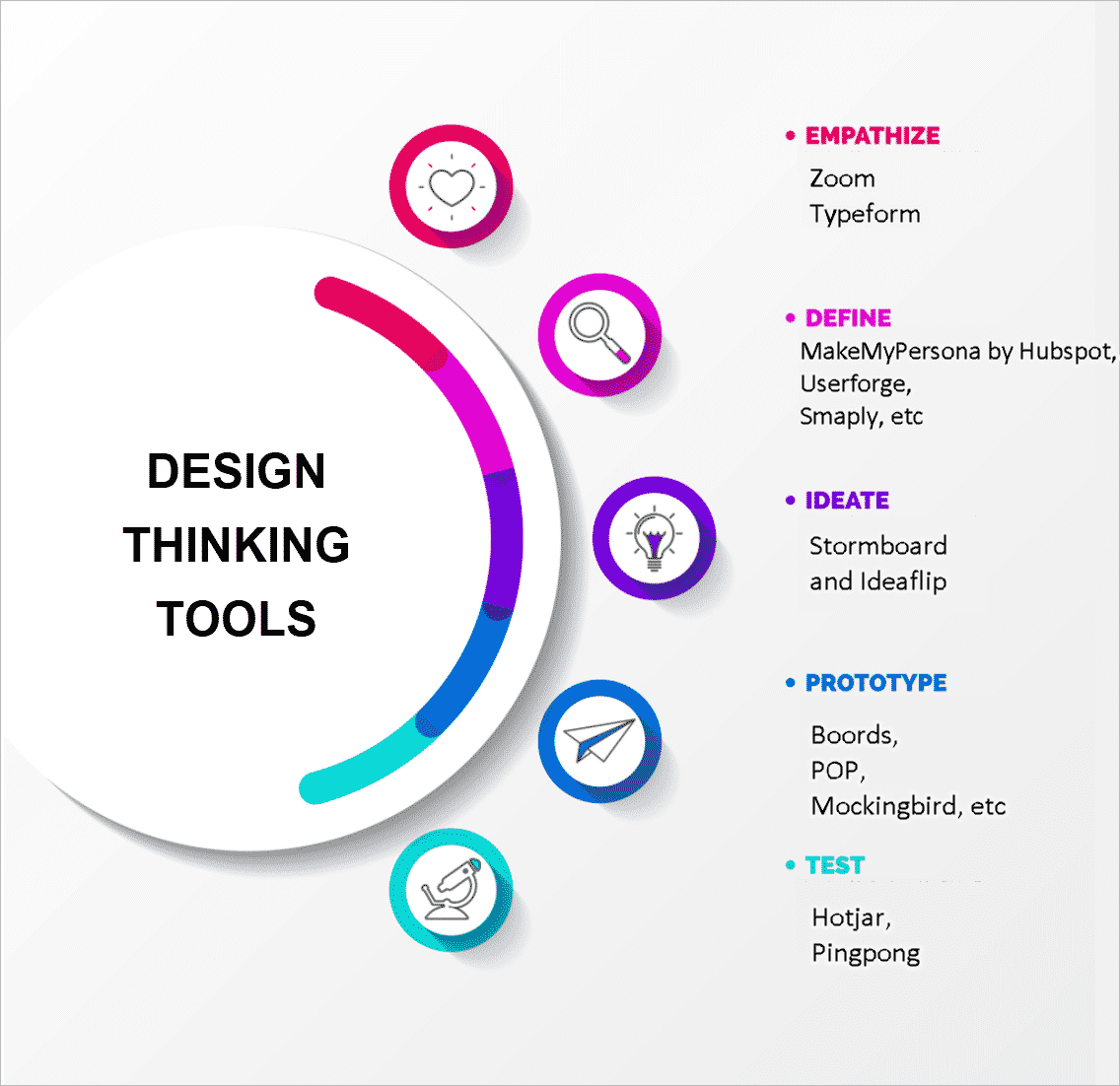
Begin by infusing primary and secondary research to create profound empathy with your customers. Construct persona maps and conduct interviews to uncover real problems, steering your solutions toward authentic customer needs. Dive into why design thinking is pivotal for creative problem-solving and your business’s overall health. The first phase of any design thinking project is getting to know your audience. Once again, it’s all about the users, so start by identifying and understanding their wants, needs, challenges, and delight moments.
Step 3. Ideate
Tim Brown sums up that design thinking provides a third way to look at problems. The fourth and final phase, implementation, is when the entire process comes together. As an extension of the develop phase, implementation starts with testing, reflecting on results, reiterating, and testing again. This may require going back to a prior phase to iterate and refine until you find a successful solution. Such an approach is recommended because design thinking is often a nonlinear, iterative process. Divergence and convergence is a human-centered design approach to problem-solving.
It’s a process that digs a bit deeper into problem-solving as you seek to understand your users, challenge assumptions and redefine problems. The main value of design thinking is that it offers a defined process for innovation. While trial and error is a good way to test and experiment what works and what doesn’t, it’s often time-consuming, expensive, and ultimately ineffective. On the other hand, following the concrete steps of design thinking is an efficient way to develop new, innovative solutions. The first, and arguably most important, step of design thinking is building empathy with users.
The purpose of Design Thinking is to produce innovative solutions that are desirable, feasible and viable. Also referred to as the Three Lenses of Human-Centered Design, these three overlapping criteria help ensure Design Thinking teams focus their efforts on creating usable products that people want. Analysis is about breaking down complex concepts and problems into smaller, easier-to-understand constituents.
It is no longer should be limited to its role as a tool, but also it should extend this role to contribute in drawing the company strategy and should be considered in every development process. Design is a process rather than a tool, and the design thinking process is a user-driven method that ensures that the final product is desirable and solves user problems. Many design thinking models were introduced to build a user-centered design. Selecting the proper model to follow depends on the complexity of the model and the size of the company. Successful companies such as Lego, IKEA, Apple, and Microsoft have applied different design thinking models to build user-centered products. Additionally, applying design thinking can help companies to improve its innovation capabilities, address complex problems, increase profit, and improve its competitiveness capabilities.
These advantages often arise because design thinking breaks a common brainstorming pattern called ingrained thinking. Design thinking is a process that has been used by institutions and businesses for years and continues to stimulate innovation and creative thinking for artists and innovators alike. Applying some structure is valuable, though — it keeps projects on track and helps those without design experience adjust to the challenging process. Toyota’s Production System (TPS) is often cited as an example of Design Thinking applied to manufacturing.
Design Council's Double Diamond diagram depicts the divergent and convergent stages of the design process. IDEO is a leading design consultancy and has developed its own version of the design thinking framework. With the foundation ready, teams gear up to “think outside the box.” They brainstorm alternative ways to view the problem and identify innovative solutions to the problem statement. Don Norman, a pioneer of user experience design, explains why the designer’s way of thinking is so powerful when it comes to such complex problems.
This is important because it aligns the team on what needs to be considered during the rest of the design thinking process. Design thinking gives teams a new way to approach their projects and overcome some of those well-known challenges. It can help teams understand their users' needs and challenges, then apply those learnings to solve problems in a creative, innovative way. Understanding design thinking can transform your team’s problem-solving approach — and how you work together. Design thinking is an iterative, non-linear process which focuses on a collaboration between designers and users. It brings innovative solutions to life based on how real users think, feel and behave.
User-centered design is great for developing a fantastic product or service. In the past, a company could coast on a superior process or product for years before competitors caught up. But now, as digitization drives more frequent and faster disruptions, users demand a dynamic mix of product and service. Emphasis has shifted firmly away from features and functions toward purpose, lifestyle, and simplicity of use. User-centered design focuses on improving a specific product or service.

No comments:
Post a Comment